Ignition coil vs spark plug: The ignition coil generates high voltage and sends it to the spark plug, which creates a spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine. Both are essential for engine performance.
The ignition system is the heart of your car’s engine, converting electrical energy into the spark needed to ignite the fuel mixture inside the combustion chamber. Two important components in this process are the ignition coil and the spark plug. While both are essential for starting and running the engine, they serve different purposes. Knowing the difference between the ignition coil and spark plug is vital for diagnosing engine problems, ensuring proper maintenance, and keeping the vehicle running smoothly.
In this article, we will explain the roles of the ignition coil and spark plug, how they work together, common issues that can arise with each, and how to maintain them.
Contents
What is an Ignition Coil?
An ignition coil is one of the primary components in the ignition system of a vehicle. Its job is to convert the low voltage from the vehicle’s battery (12 volts) into the high voltage needed (up to 45,000 volts) to fire the spark plugs and ignite the air-fuel mixture inside the engine’s cylinders. The ignition coil ensures that the spark plug receives the correct voltage at the correct moment to make sure the engine fires properly.
Key Functions of the Ignition Coil:
- Voltage Conversion: The ignition coil’s main function is to step up the voltage from the battery, transforming it from the low 12 volts to the higher voltage required to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine.
- Spark Timing: It works in conjunction with the engine control unit (ECU) to precisely time when to deliver the electrical charge to the spark plug.
- Spark Delivery: The ignition coil delivers the high-voltage electrical pulse directly to the spark plug, which in turn creates a spark to ignite the fuel mixture.
Types of Ignition Coils:
- Traditional Coil: Older vehicles often use a single ignition coil to deliver voltage to all the spark plugs.
- Coil-on-Plug (COP): Modern vehicles often use a COP system, where each cylinder has its own ignition coil. This setup offers greater efficiency and performance by providing more precise timing for each spark plug.
Common Issues with Ignition Coils:
- Misfires: A faulty ignition coil will fail to send sufficient voltage to the spark plugs, resulting in engine misfires.
- Decreased Performance: A malfunctioning ignition coil can cause a loss of power and acceleration due to incomplete combustion.
- Difficulty Starting the Engine: If the ignition coil isn’t working properly, the engine may have trouble starting or may not start at all.

What is a Spark Plug?
A spark plug is a small but crucial part of the vehicle’s ignition system. It receives the high-voltage electricity from the ignition coil and converts it into a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s combustion chamber. This spark is what powers the engine, turning the energy stored in the fuel into mechanical energy that moves your vehicle.
Key Functions of the Spark Plug:
- Spark Creation: The spark plug creates the spark necessary for ignition by using the high-voltage energy delivered by the ignition coil.
- Heat Dissipation: The spark plug helps to dissipate the heat generated during the combustion process. The heat is transferred from the combustion chamber to the cooling system of the vehicle.
- Efficient Combustion: A properly functioning spark plug ensures that combustion occurs at the optimal time, helping the engine run efficiently.
Types of Spark Plugs:
- Copper Spark Plugs: These are affordable and offer excellent conductivity, but they tend to wear out faster.
- Platinum Spark Plugs: They last longer than copper spark plugs and offer better performance.
- Iridium Spark Plugs: The most durable option, providing the longest lifespan and the best performance, especially in modern engines.
Related Article
Which Spark Plug is Best Iridium or Platinum?
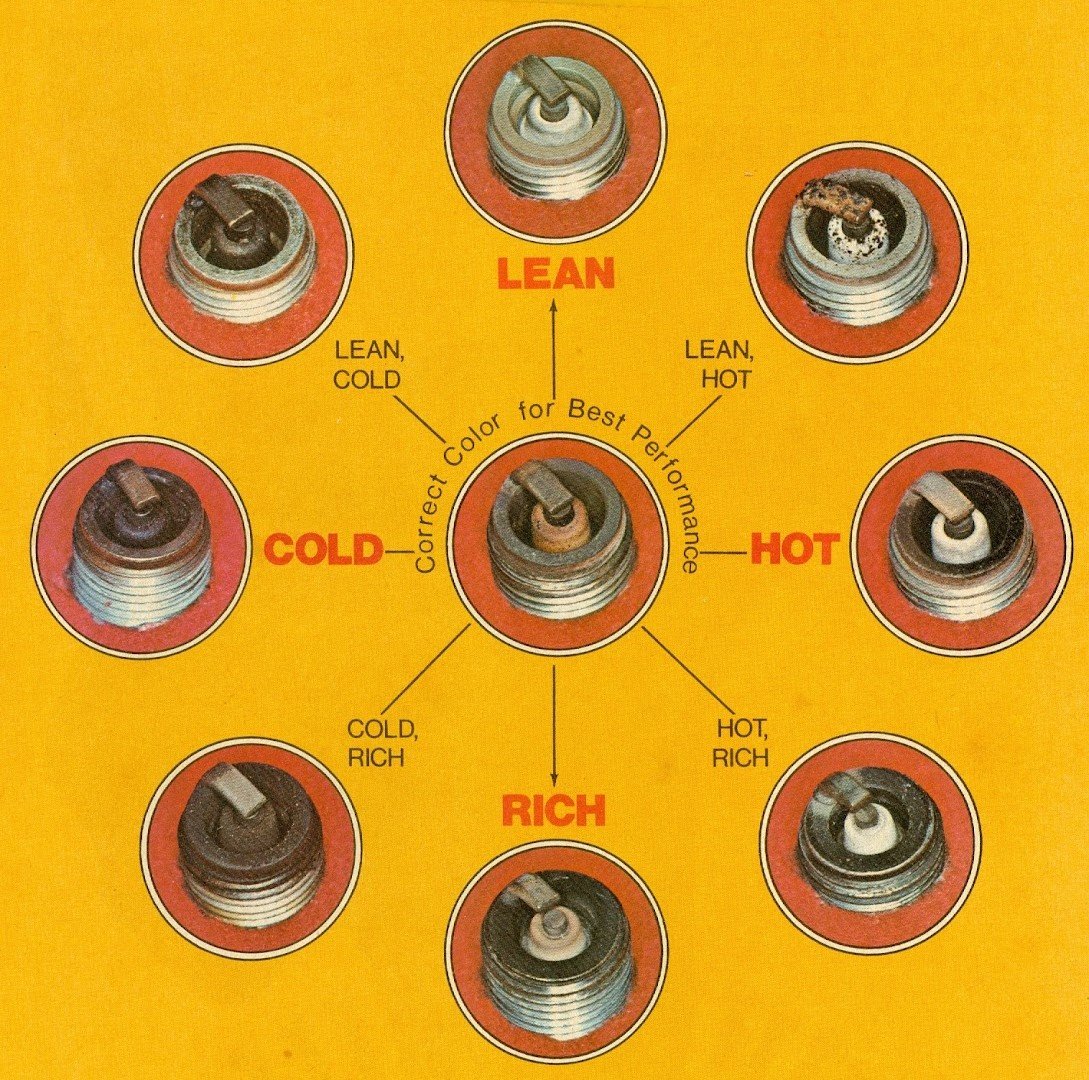
Common Issues with Spark Plugs:
- Worn Electrodes: Over time, the electrodes on a spark plug wear down, leading to weak or irregular sparks.
- Fouling: Fouling occurs when carbon deposits build up on the spark plug, which can cause the engine to misfire or fail to start.
- Rough Idling: Bad spark plugs can lead to rough engine idle or even stalling.
- Poor Acceleration: If the spark plugs are damaged or worn out, you might notice reduced power when accelerating.

Ignition Coil vs Spark Plug: How They Work Together
The ignition coil vs. spark plug dynamic is an important one to understand. While they have different functions, they rely on each other to ensure the engine runs efficiently. Here’s how they work together:
- Ignition Coil Generates Voltage: The ignition coil takes the 12-volt power from the vehicle’s battery and converts it into high-voltage electricity (up to 45,000 volts).
- Voltage Sent to the Spark Plug: This high voltage is delivered to the spark plug, which then uses it to create a spark inside the combustion chamber.
- Ignition of the Air-Fuel Mixture: The spark created by the spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, powering the engine.
If the ignition coil fails to send the required voltage to the spark plug, the spark plug won’t fire, and the engine will fail to start or misfire. Similarly, if the spark plug is worn or damaged, it won’t create the spark needed for proper combustion, resulting in engine inefficiency or failure.
Diagnosing Issues: Ignition Coil vs Spark Plug
When it comes to diagnosing issues with the ignition system, it can be challenging to determine whether the problem lies with the ignition coil or the spark plug. However, here are some key diagnostic steps to help you figure it out:
Diagnosing Ignition Coil Issues:
- Engine Misfires: If your engine is misfiring, the issue may be with the ignition coil not sending enough voltage to the spark plug.
- Loss of Power: A faulty ignition coil can result in a noticeable loss of engine power, especially when accelerating.
- Rough Starting: If the engine is difficult to start or fails to start altogether, it could be due to an ignition coil issue.
- Check Engine Light: A malfunctioning ignition coil may trigger the check engine light, which can be diagnosed with a scan tool.
Diagnosing Spark Plug Issues:
- Engine Misfires: Misfires often result from faulty spark plugs. You may notice the engine shaking or sputtering, especially during acceleration.
- Poor Acceleration: If the car is sluggish when accelerating, it could be due to worn-out spark plugs.
- Rough Idling: If your engine idles roughly, this could indicate that one or more of your spark plugs are faulty.
- Excessive Fuel Consumption: A bad spark plug can lead to inefficient fuel combustion, resulting in poor fuel economy.
How to Maintain Ignition Coils and Spark Plugs
Proper maintenance of both ignition coils and spark plugs is essential for keeping your engine running smoothly and avoiding costly repairs. Here are some tips for maintaining these crucial components:
Ignition Coil Maintenance:
- Regular Inspection: Check for physical damage to the ignition coil. Look for cracks, corrosion, or burn marks on the coil and connectors.
- Replace Worn Coils: If one ignition coil fails, it’s often a good idea to replace the others to ensure uniform performance across all cylinders.
- Keep the Engine Clean: Regular cleaning of the engine components, especially around the ignition coils, helps prevent dirt and moisture buildup that could affect their performance.
Spark Plug Maintenance:
- Replace Spark Plug Regularly: Spark plugs should typically be replaced every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the type of spark plug and your vehicle’s specifications.
- Inspect for Wear: Remove the spark plugs periodically to check for excessive wear, carbon buildup, or oil fouling.
- Check Spark Plug Gap: Ensure that the spark plug gap is within manufacturer specifications to ensure proper ignition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about ignition coil vs spark plug –
1. What is the main function of an ignition coil?
The ignition coil converts the 12-volt electrical current from the car’s battery into a high-voltage charge that is delivered to the spark plugs to create a spark and ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine.
2. Can a bad ignition coil cause engine misfires?
Yes, a bad ignition coil can cause engine misfires, poor acceleration, and difficulty starting the engine.
3. What are the signs that a spark plug needs to be replaced?
Signs that a spark plug needs to be replaced include engine misfires, poor acceleration, rough idling, and decreased fuel efficiency.
4. Is it necessary to replace ignition coils and spark plugs at the same time?
While it’s not mandatory, replacing ignition coils and spark plugs at the same time can ensure optimal performance and prevent uneven firing across the cylinders.
Conclusion
Both the ignition coil vs. spark plug are vital components of the vehicle’s ignition system, and understanding their differences and how they work together is essential for keeping your engine running smoothly. The ignition coil’s job is to generate high voltage, while the spark plug is responsible for creating the spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine. Both parts are indispensable, and when one fails, the engine will struggle to perform properly.