No spark from spark plug happens when the ignition system fails to deliver a spark. Common causes include faulty coils, damaged wires, or worn spark plugs.
It’s frustrating when the engine cranks but does not start. You may think that there is no spark at the spark plug. The no-spark troubleshooting situation is commendable especially if the goal is to avoid paying the mechanic off for a lot of money. You do not need to pay off a mechanic for a lot of money to figure this one out. In this case, this The different reasons, symptoms, diagnoses and solutions to addressing the no-spark cases as they pertain to the spark plug issue will be addressed thoroughly and systematically within this guide.

Contents
- 1 What Does “No Spark from Spark Plug” Mean?
- 2 Common Causes of No Spark at the Spark Plug
- 3 How to Diagnose No Spark at the Spark Plug
- 3.1 Step 1: Safety First
- 3.2 Step 2: Check for Spark
- 3.3 Step 3: The Ignition Coil
- 3.4 Step 4: Check The Spark Plug Wires
- 3.5 Step 5: The Sensors Of The Crankshaft And The Camshaft
- 3.6 Step 6: Review the Control Module
- 3.7 Step 7: Check Parts Of the Distributor
- 3.8 Step 8: Check Relays and Fuses
- 3.9 Fixing the No Spark Issue
- 4 Preventative Maintenance Tips
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 6 Conclusion
What Does “No Spark from Spark Plug” Mean?
If there is no spark from the spark plug, then no matter how long you attempt cranking, your vehicle will not move an inch. Unfortunately, that is the case if you do not possess a working vehicle. The engine does not have the electric current needed to power the spark plug.
When an engine refuses to turn over, that is always a tough puzzle to solve. While everyone always has a unique answer, reason, explanation, or a way to solve the case, the truth is that many of them do not solve the problem. Let’s analyze some of the most popular and well reputed reasons for this phenomenon.
Common Causes of No Spark at the Spark Plug
If your engine is cranking but you’re not getting any spark at the spark plug, it could be due to a number of reasons within the ignition system. Let’s explore the most common causes that could be responsible for this issue.
1. Broken Ignition Coil
An ignition coil carries the burden of the production of sparks and is responsible for everything spark-related. She is in charge of taking the low voltage (12 volts) charge coming from the car battery and transforming it to the magnitudes (thousands) that trigger the ignition of the spark plug.
If an ignition coil is broken or damaged, she does not have the power to trigger the spark plug. Tell tale signs an ignition coil is damaged or broke: the car is suffering from engine “misfires”, “rough” idling, or has low “economy” with regards to “fuel”.
How to diagnose:
- Coils with discontinuities within the circuit have either excessively low or high resistance values. A faulty coil can simply be replaced.
- Burnt coils, cracked coils or corroded coils should be examined more closely.
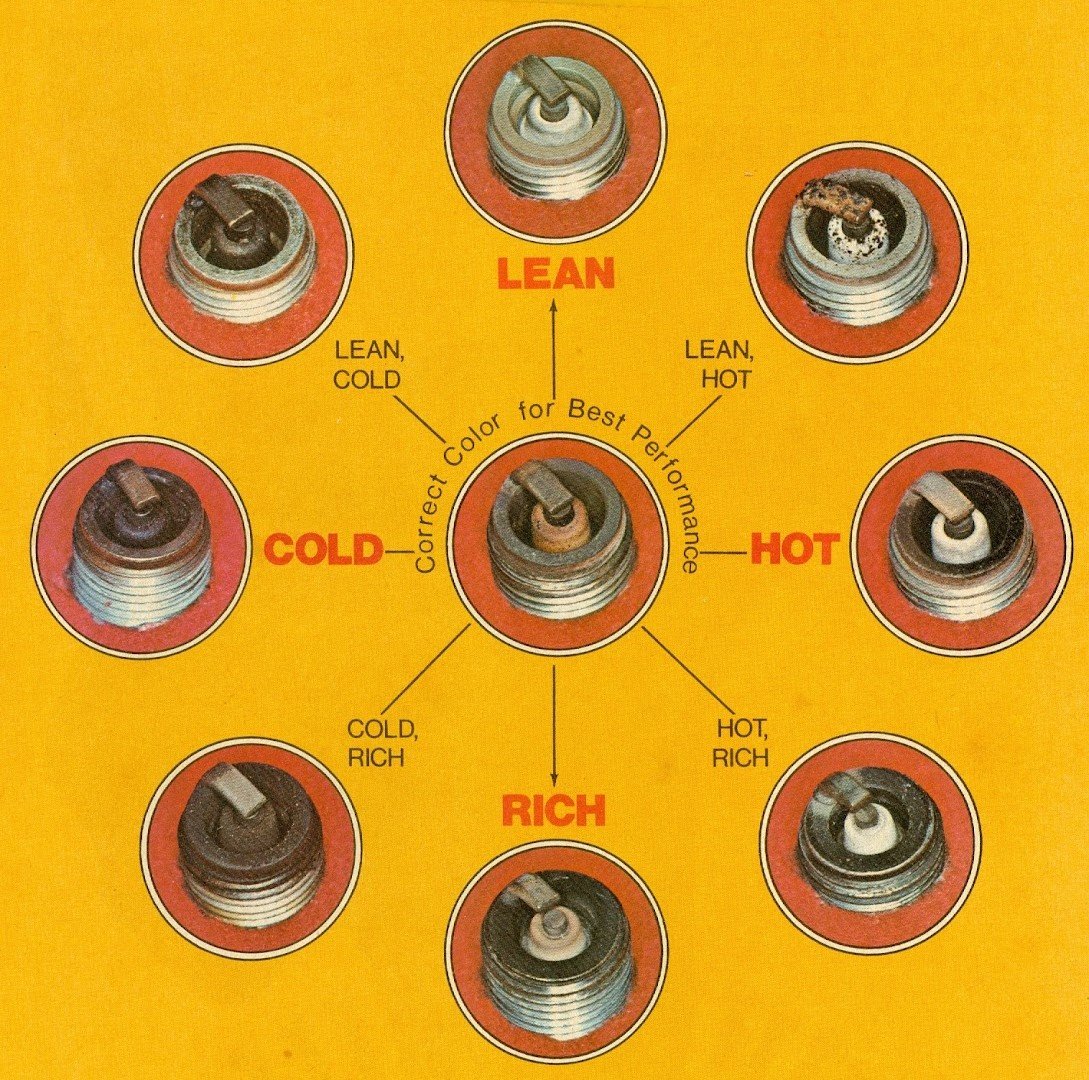
2. Worn or Damaged Spark Plugs
Spark plugs can wear out over time due to prolonged use, corrosion, or carbon buildup. When spark plugs are worn out, they lose the ability to generate a strong spark, which may result in the engine not starting at all.
How to diagnose:
- If the electrode is worn down or there is significant carbon buildup, the spark plug should be replaced.
- Remove the spark plug and inspect it for signs of wear or corrosion.
3. Worn Out Spark Plugs
The ignition comes from the coil and is transferred via the spark plug wires. High voltage is sent from the ignition coil to the spark plug through the wires. If the spark plug wires are cracked, corroded or otherwise damaged, the voltage is unable to reach the spark plug, resulting in the absence of a spark.
How to assess:
- Visually inspect the wires for cracking, fraying, or other signs of damage.
- Check the wires with the use of a spark tester to see if any output is detected as well as to see if spark flow is present.
4. Issues with the Crankshaft or Camshaft Position Sensors
Both the crankshaft and camshaft have sensors that monitor the angle and position. This is used so the ECU is capable of determining the order of ignition to have the engine running. When these sensors are faulty, it is a safe assumption that the ECU will have a hard time determining the proper order of ignition and spark, thus having a no spark situation.
How to assess:
- Using an OBD II scanner and plugging it into the vehicle, see if any crank or camshaft position sensor error codes pop up.
- Check the sensor’s resistance with a multimeter and make sure its resistance is within the quoted values for the sensor.
5. Failure of the Ignition Control Module
The ICM is in charge of the timing of the spark and the moment the spark happens. With the engine crankshaft and camshaft sensors, the ICM makes certain the spark happens in the proper order. If the spark module is broken, there will be no sparks at the ignition coil. There will also be no sparks at all.
Diagnosing process:
- Use a multimeter to gauge the module, then check the module’s resistance against the ICM manufacturer’s specs.
- The faulty module isn’t worth repair. It should be replaced at once.
6. Damaged capacitor
Cars from a past era, which might still use a distributor ignition system, have parts like the rotor and the distributor cap that may become worn, cracked, or capped. This is due to the components solely responsible to send spark to the target cylinder. If these parts are damaged, the result will certainly be a no spark condition.
Diagnosing process:
- Remove the cap from the dis and inspect the parts for proper functioning.
- Look for cracks and corrosion in the rotor.
7. Blown fuses or Faulty Relays
By preventing the occurrence of short circuits and overcurrent incidents, fuses and relays confirm and guarantee the scenario that allows the ignition systems to work and keep. An ignition system that is powered by a blown fuse or a broken relay is a shy system. If the fuse is malfunctioning or blown, the ignition systems powered by the relay also malfunction. The relay also fails to ignite the spark plug with the spark needed to start the ignition and the system dies.
How to diagnose:
- In continuity fuses, ignition system fuses must be all checked.
- Relays should also be checked with a multimeter to confirm that they are functioning properly.
How to Diagnose No Spark at the Spark Plug
To diagnose, check if there is a plug in the system. First check the systems themselves, then the system with spark and the procedure.
Below are the potential solutions for the described challenge:
Step 1: Safety First
This step is described from the perspective of a workplace where there is a need to carry out a completed installation of a wireless operation system which includes integration of the electronic system. The system should be designed to ensure there is no hovered electrical voltage or incidental shorting of circuits. In order to ensure safety:
No other objects should be part of the surroundings which can be able to trigger the ignition or disturb the sequence of the sequence from the start and the rest.
Defining the system and placing gear measurement apparatus should be done in a way to ensure there positioning is safe from all other objects in the surroundings. In the case of autocratic device ignition or other related sequences starting for the device poses a danger.
There is a need to measure each of the relays with a multimeter to determine if they are able to relay on the set conditions.
Step 2: Check for Spark
To determine if there’s spark at the spark plug, follow these steps:
- Remove one of the spark plugs from the engine.
- Reconnect it to its spark plug wire.
- Hold the spark plug close to a metal part of the engine (make sure it’s grounded).
- Crank the engine and observe the spark plug. If you see a strong blue spark, the ignition system is working. If there’s no spark, proceed with further diagnostics.
Step 3: The Ignition Coil
In most cases, the source of no spark is the ignition coil. Using a multimeter, evaluate the primary and secondary resistance of the coil. If the service manual parameters is exceeded, the coil will need replacement.
Step 4: Check The Spark Plug Wires
It is vital to look at the spark plug wires for burns, cracks, and overall damage. If there are any cracks, the wires should be replaced. A spark tester can be used to determine if the wires are hot. If there is no spark, the wires should be replaced.
Step 5: The Sensors Of The Crankshaft And The Camshaft
These two sensors during ignition are crucial. If there is any disturbance, the ignition will not spark at the right time.
Using a multi tester, check the resistance and test the codes using the OBD-II scanner.
Step 6: Review the Control Module
The ignition control module, if faulty, can also cause no-spark situations. The testing should be done within the limitations set by the manufacturer on the modules’ test configuration. The module will be deemed faulty and subsequently replaced if the testing is inconclusive.
Step 7: Check Parts Of the Distributor
If your car has a distributor based ignition system, then you will need to take the distributor’s cover off. Check the cover, looking for cracks, damage, signs of wear and other possible harms. The rotor and the internal components should be checked for any problems as well. Any and all parts, no matter how small, displaying signs of damage should be thrown away.
Step 8: Check Relays and Fuses
Start by methodically assessing every fuse connected to the ignition system, and see if any have blown. This can take time, but any blown fuses should be replaced. Also, relays should be checked to ensure they are functioning.
Fixing the No Spark Issue
Next step is defining any additional repairs for the broken component, starting with its primary diagnosis. Tackle the issue with the below steps, especially if the system architecture needs modification.
Replacement of the following components is what we refer to the Coils Replacement Policy:
- Coil Ignition: An assigned component needs to be Ignition Coil. An additional step is performing a resistance test.
- Plugs Spark: An assigned component in this instance is Spark Plugs. Those that are worn or damaged are to be replaced with new ones based on the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Wires Plug Spark: In this instance, a Plug Spark Wire is the assigned component. Those found to be cracked or corroded are of no use and must be disposed of.
- Sensors and Ignition Control Module: Any sensors that are damaged plus the ignition control module must be replaced to restore the proper ignition timing.
- Distributor Components: Any parts on the distributor that are damaged plus broken caps and rotors must be replaced.
- Fuses and Relays: Replace any blown fuses or broken relays.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
To avoid the phenomenon of no spark repetition, the following methods can be called as deemed fit:
- Regularly Inspect Spark Plugs and Wires: Inspect any worn out wires and spark plugs, and ineffective spark plug wires on border to wire meters. Replace them seamlessly if deemed appropriate.
- Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedule: Follow the timeline to change ignition parts.
- Protect Parts (Corrosion Control, Parts, System): Corrosion and debris on the ignition coil and distributor contain components that need maintenance.
- Components and Parts: Always choose the replacement windows that say meet and exceed the specifications drawn from the manufacturer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about no spark from spark plug –
How can I tell if my ignition coil is bad?
Using a device called a coil meter, and measuring the primary and secondary resistance, helps gauge the functionality of the coil. If it is broken, than it is due for a replacement.
Does a broken spark plug leads tp a spark gap?
Yes, a broken spark plug creates a spark gap, which can lead to problems during start up because it is damaged or worn and does not produce the spark.
How do I go about troubleshooting if my ignition coil is not faulty?
If the ignition coil is not faulty, check other components; spark plug wires, sensors, or the ignition control module.
How often should spark plugs be replaced??
The average timeline for replacing spark plugs is every 30,000 to 50,000 miles stipulating the need to check the vehicle’s service manuel for more precise data.
Driving a car with a broken ignition coil: is it possible or not?
A car with a broken ignition coil is a car that cannot be driven. Ignition coils that are broken will lead to the malfunctions of the engine, higher fuel consumption, as well as directly damaging other components in the ignition system.
Conclusion
Understanding the reason as to why the spark plug is not working does not necessarily mean that one has to go to a mechanic. Most people do not know this, as resolving such issues is fairly common. If you are aware of the car’s ignition system and the reason why it does not spark, you will be able to troubleshoot the issue.
You should also note that doing diagnosis alone is not the best of ideas, because this can be very dangerous. Other people should also minimize the need to go to a mechanic just to be safe every once in a while. Performing the proper maintenance to the ignition system will guarantee that the engine starts without a hitch.