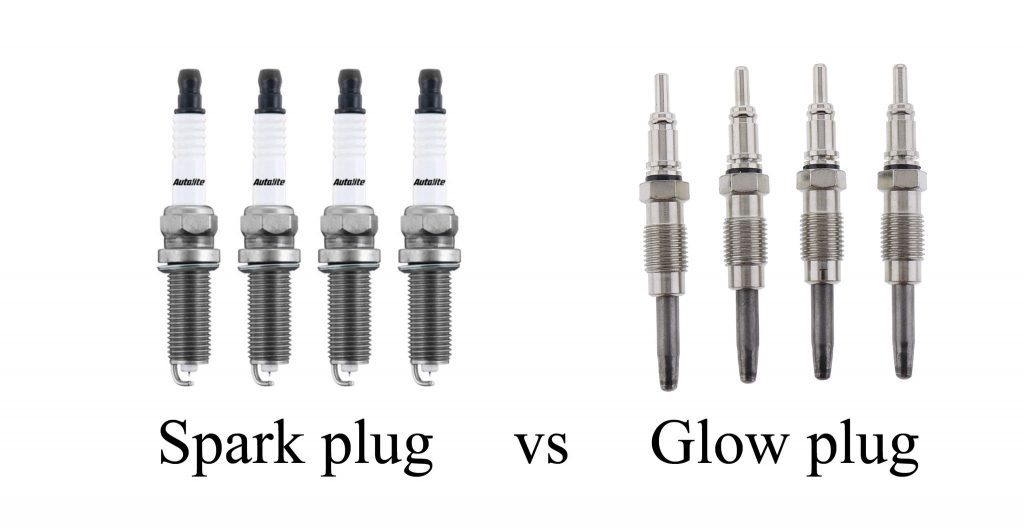
Glow plug vs spark plug: Glow plugs heat the combustion chamber in diesel engines for cold starts, while spark plugs create a spark to ignite the fuel in gasoline engines. The key difference is their role in the ignition process for different engine types.
When you start a vehicle, whether it’s a diesel truck or a gasoline car, there’s one thing common between both engines: the need for ignition. However, the way ignition happens varies significantly between the two engine types. While the concept of ignition is universal, the tools that make it happen differ: glow plugs in diesel engines and spark plugs in gasoline engines.
In this article, we will explain the glow plug vs spark plug debate, exploring what each one does, their differences, how they work, and their significance in the engine’s performance. If you’ve ever wondered why these two components are essential and how they operate in their respective engine types, this guide will explain it all.
Contents
What is a Glow Plug?
A glow plug is a heating element used in diesel engines to assist with the ignition process during cold weather starts. Diesel engines do not use spark plugs like gasoline engines. Instead, they rely on compression ignition, meaning that the air inside the engine is compressed to high pressure, generating heat that ignites the fuel. However, in colder conditions, the air temperature may not be high enough to ignite the diesel fuel easily. This is where the glow plug plays a critical role.
How Does a Glow Plug Work?
The purpose of a glow plug is to pre-heat the combustion chamber to facilitate proper ignition of the diesel fuel. When the engine is started, the glow plug heats up, helping to raise the temperature in the combustion chamber. This makes the ignition process smoother and more efficient, particularly in cold climates. The glow plug does this by heating up to a red-hot temperature, usually around 800°C to 1,000°C, to aid in starting the engine.
Glow plugs are activated when the ignition is turned on, and they stay active only for a short period until the engine reaches a certain temperature. Once the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature, the glow plug shuts off, as it is no longer required to assist in the combustion process.
Glow Plug Construction and Materials
Glow plugs are designed to endure high temperatures. They come in various types based on the materials used:
- Metal Glow Plugs: Typically used in older diesel engines, these glow plugs are made from metal materials such as steel or copper. They take longer to heat up but are durable.
- Ceramic Glow Plugs: Found in more modern diesel engines, these glow plugs are made of ceramic material. They are faster at heating up and more efficient compared to metal glow plugs, making them ideal for contemporary diesel engine technology.
What is a Spark Plug?
A spark plug, in contrast to a glow plug, is a crucial component used in gasoline engines to ignite the air-fuel mixture inside the engine. Gasoline engines rely on spark ignition, meaning the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark produced by the spark plug, causing combustion. This is entirely different from diesel engines, which rely on high compression to generate heat.
How Does a Spark Plug Work?
A spark plug’s job is to generate an electric spark when the engine is running. This spark ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber at the precise moment when the compression reaches its peak. This ignition is necessary for the engine to produce power, which drives the vehicle.
Spark plugs work continuously throughout the engine’s operation, producing sparks during each combustion cycle. This ensures that the engine runs smoothly, generating the necessary power to propel the car forward. The ignition cycle is an ongoing process in gasoline engines, unlike the short-term role of glow plugs in diesel engines.
Spark Plug Construction and Materials
Spark plugs are made up of several key components:
- Electrode: The central electrode is responsible for creating the spark. It is made from durable materials such as copper, platinum, or iridium.
- Insulator: Surrounding the electrode, the ceramic insulator helps to protect the spark plug from heat and provides insulation to the electric current.
- Shell: The steel casing around the spark plug allows it to attach to the engine cylinder head and provides protection to the inner components.
Spark plugs are built to withstand high temperatures and pressures within the combustion chamber. They are essential for the engine’s performance and fuel efficiency.
Glow Plug vs Spark Plug: The Key Differences
Now that we have a detailed understanding of what each component does, let’s look at the key differences between glow plugs and spark plugs in terms of their function, material, and usage.
1. Function
- Glow Plug: The primary function of a glow plug is to heat the combustion chamber in diesel engines, especially in cold weather. It helps the diesel fuel ignite by pre-heating the air inside the chamber.
- Spark Plug: A spark plug, on the other hand, creates a high-voltage spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in a gasoline engine, allowing for the combustion process to begin.
2. Engine Type
- Glow Plug: Used in diesel engines, where the engine relies on compression ignition.
- Spark Plug: Found in gasoline engines, where the engine operates using spark ignition.
3. Operating Temperature
- Glow Plug: Glow plugs heat up to extremely high temperatures (around 800°C to 1,000°C) but are only active during the startup phase of the engine.
- Spark Plug: Spark plugs generate a high-voltage spark during each ignition cycle, but they do not heat up to the same extreme temperatures as glow plugs.
4. Usage Time
- Glow Plug: Glow plugs are only active during engine startup, particularly in cold weather conditions, and deactivate once the engine reaches its optimal temperature.
- Spark Plug: Spark plugs operate continuously during the engine’s normal running cycle, creating sparks to ignite the fuel during every combustion event.
5. Material and Construction
- Glow Plug: Glow plugs are generally made from metal or ceramic, designed to withstand high temperatures for short durations.
- Spark Plug: Spark plugs are made of materials like copper, platinum, or iridium and must endure high temperatures and pressures continuously during engine operation.
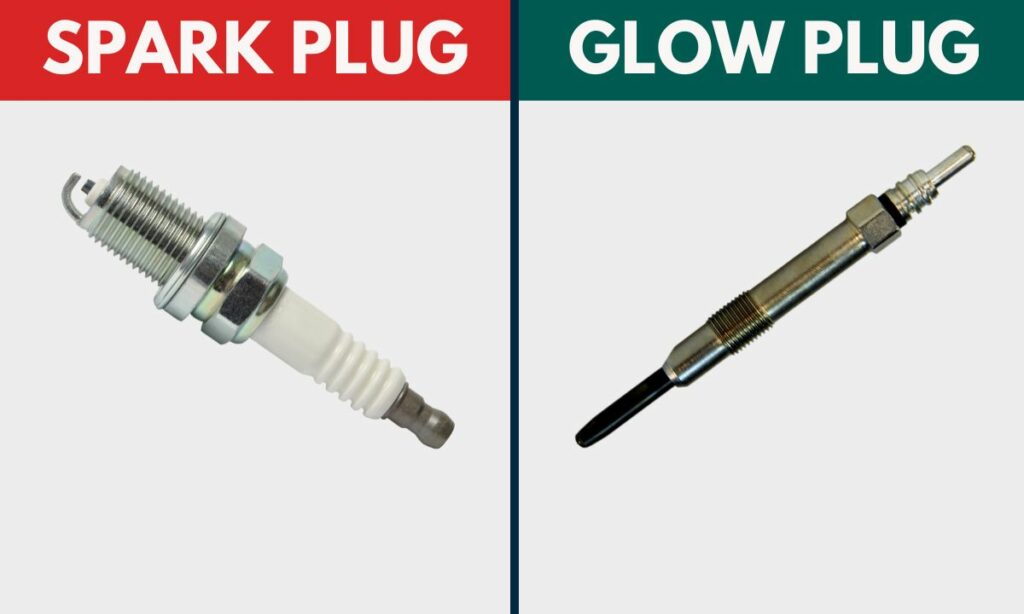

Importance of Glow Plugs in Diesel Engines
In diesel engines, the efficient operation of glow plugs is crucial for starting the engine in cold conditions. Without the glow plugs, it would be very difficult to ignite the fuel, particularly when the temperature is low. Diesel engines rely on compression ignition, and the glow plug assists by raising the temperature to a level where combustion can take place. This ensures that the engine starts efficiently, without excessive fuel consumption or strain on the battery.
Importance of Spark Plugs in Gasoline Engines
Spark plugs are the lifeblood of gasoline engines. They ensure that the air-fuel mixture ignites correctly during each combustion cycle. This precise ignition is vital for maintaining the engine’s fuel efficiency, power output, and overall performance. A faulty spark plug can lead to poor acceleration, reduced engine performance, and higher emissions.
Maintaining Glow Plugs
Glow plugs are generally reliable but require periodic checks and replacements. Over time, they can become worn, and their performance may decline. Regularly check for signs of difficulty starting, especially in colder weather, and replace faulty glow plugs promptly.
- Signs of Faulty Glow Plugs: Difficulty starting, rough engine idle at startup, and increased fuel consumption.
- Replacement Interval: Glow plugs typically need to be replaced every 100,000 to 150,000 miles.
Maintaining Spark Plugs
Spark plugs need regular inspection and replacement to keep the engine running smoothly. Over time, the spark plug electrodes can wear out or become fouled by deposits, leading to poor engine performance.
- Signs of Faulty Spark Plugs: Misfires, poor acceleration, rough idling, and trouble starting the engine.
- Replacement Interval: Spark plugs should generally be replaced every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the vehicle and type of spark plug.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about the difference between a glow plug and a spark plug –
1. Can I drive a diesel engine without glow plugs?
While the engine will run, it will struggle to start, especially in cold weather, without functional glow plugs.
2. How often should I replace glow plugs?
Glow plugs typically need to be replaced every 100,000 to 150,000 miles.
3. Can faulty spark plugs affect fuel economy?
Yes, faulty spark plugs can cause incomplete combustion, leading to poor fuel efficiency.
4. Why do I need to replace my spark plugs?
Over time, spark plugs wear out, and faulty spark plugs can lead to misfires, rough idling, poor acceleration, and higher emissions.
Conclusion
Glow plugs and spark plugs serve similar yet distinctly different roles depending on the type of engine. Glow plugs are crucial for diesel engines, especially in colder conditions, while spark plugs are essential for gasoline engines to facilitate ignition. Both are vital for optimal engine performance, and maintaining them is key to ensuring efficient combustion and a smooth driving experience.
Whether you own a diesel or gasoline-powered vehicle, understanding these components and keeping them well-maintained will not only help you avoid unnecessary engine issues but will also extend the life of your vehicle.