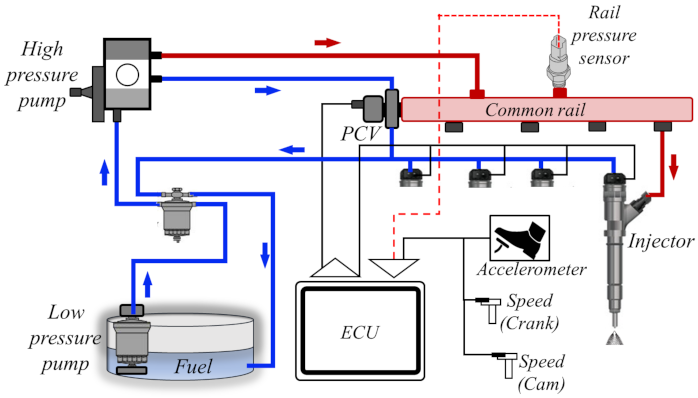
Why spark plug is not used in diesel engines: Spark plugs are not used in diesel engines because diesel engines rely on compression ignition rather than spark ignition. The high compression in the engine generates enough heat to ignite the diesel fuel, eliminating the need for a spark plug to trigger combustion.
Have you ever wondered why diesel engines don’t use spark plugs, unlike their gasoline counterparts? The answer lies in the fundamental differences in how the two types of engines operate. While gasoline engines rely on spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture, diesel engines use compression ignition, where the heat from compressed air triggers fuel combustion.
In this article, we will explain why spark plugs are not used in diesel engines, how diesel engines work, and what makes them unique compared to gasoline engines.
Contents
The Role of Spark Plugs in Gasoline Engines
In gasoline engines, spark plugs are important for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. Here’s how they work:
1. Ignition Process in Gasoline Engines
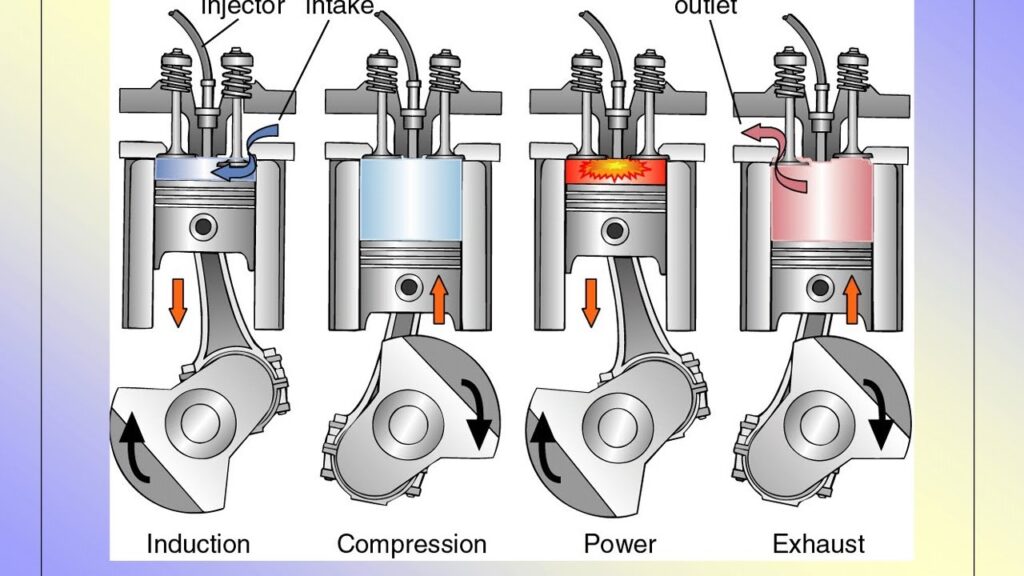
In a gasoline engine, the air-fuel mixture is compressed in the engine’s cylinders and then ignited by an electric spark created by the spark plug. This spark causes the fuel to combust, powering the engine. Gasoline engines rely on spark plugs to start the combustion process.
2. Need for Spark Plug in Gasoline Engines
Gasoline engines use spark plugs because the fuel-air mixture in the cylinders needs an external source of ignition. The spark plug provides the spark necessary to ignite the mixture at the correct time, creating controlled combustion and delivering power to the engine.
How Diesel Engines Operate Differently
Diesel engines function on a different principle compared to gasoline engines. Instead of using spark plugs to ignite the fuel, diesel engines rely on compression ignition. Let’s break down the key elements of this process:
1. Compression Ignition in Diesel Engines
In a diesel engine, air is compressed within the cylinder at much higher pressures and temperatures compared to a gasoline engine. This compression causes the air temperature to rise significantly. When the diesel fuel is injected into this high-temperature, high-pressure environment, it spontaneously ignites without the need for a spark plug.
The ignition is due to the heat generated from the intense compression, and this is why spark plugs are unnecessary in diesel engines.
2. Higher Compression Ratio
Diesel engines have a higher compression ratio than gasoline engines, meaning that the air-fuel mixture is compressed to a much smaller volume. This higher compression generates enough heat to ignite the diesel fuel automatically, making spark plugs redundant.
3. The Importance of Fuel Injection
Diesel engines use direct fuel injection, where fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber at high pressure. This precise injection, combined with the high compression ratio, leads to ignition, without requiring an external ignition source such as a spark plug.
Advantages of Diesel Engines Not Using Spark Plugs
Now that we know why diesel engines don’t use spark plugs, let’s look at some of the advantages of this design:
1. Increased Efficiency
Diesel engines are generally more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines because they operate at higher compression ratios. The lack of a spark plug simplifies the design of the engine, and the compression ignition system improves the overall fuel economy. Diesel engines extract more energy from the fuel, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as trucks, buses, and industrial machinery.
2. Durability and Longevity
Diesel engines are built to withstand higher pressures and temperatures due to the nature of compression ignition. The absence of spark plugs reduces the risk of wear associated with electrical components, making diesel engines more durable and longer-lasting. They are known to have a longer lifespan compared to gasoline engines.
3. Lower Emissions of CO2
Though diesel engines can produce higher levels of NOx and particulate matter, they tend to emit lower levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) compared to gasoline engines. This is because they are more fuel-efficient, meaning less fuel is required to generate the same amount of energy.
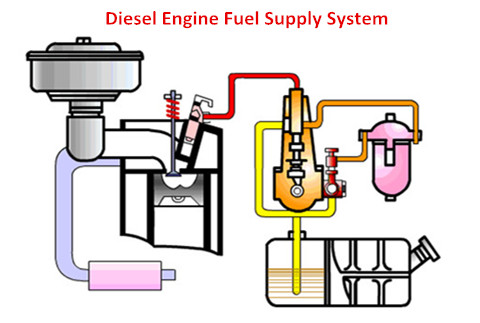
Spark Plug vs. Diesel Fuel Injector
While spark plugs play a key role in gasoline engines, diesel engines rely on fuel injectors to initiate combustion. Here’s a comparison of their roles:
1. Spark Plug in Gasoline Engines
- Function: Provides an electric spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
- Ignition Method: Electrical spark.
- Fuel Type: Gasoline (mixed with air).
- Engine Type: Gasoline engines.
2. Diesel Fuel Injector
- Function: Injects fuel directly into the combustion chamber under high pressure.
- Ignition Method: Compression ignition (spontaneous combustion due to heat).
- Fuel Type: Diesel fuel.
- Engine Type: Diesel engines.
Unlike spark plugs, which are used in gasoline engines for ignition, fuel injectors in diesel engines inject fuel at precisely the right moment into highly compressed air, igniting it naturally without the need for spark plugs.
Why Diesel Engines Don’t Need Spark Plugs
There are several key reasons why diesel engines do not require spark plugs:
1. Self-Ignition through Compression
As mentioned earlier, diesel engines rely on compression ignition. The air is compressed to a high pressure, causing it to heat up. When the diesel fuel is injected, it ignites due to the heat from compression. Spark plugs are not necessary because the engine’s design is tailored for this high-temperature self-ignition process.
2. Different Engine Design
Diesel engines have a much higher compression ratio than gasoline engines, which generates the heat necessary for ignition. The high compression ratio in diesel engines makes it impossible to use spark plugs, which would not be able to withstand such intense conditions.
3. Spark Plug Alternatives
Instead of spark plugs, diesel engines rely on components like glow plugs to help with starting in cold weather. Glow plugs warm up the air inside the combustion chamber to ensure the fuel ignites when the engine is started, but these plugs do not perform the same function as spark plugs in gasoline engines.
Related Article
Can Spark Plug Wires Cause Misfire?
Are Spark Plug Wires Interchangeable?
Are Spark Plug Sockets Universal?
Are Spark Plug Wires Universal?
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about causes of spark plug not used in diesel engines –
1. Can a diesel engine run with spark plugs?
No, a diesel engine is designed to run without spark plugs. Diesel engines use compression ignition rather than a spark to ignite the fuel.
2. Why do diesel engines need glow plugs?
Glow plugs are used in diesel engines to help with starting the engine in cold conditions by heating the air inside the cylinder to aid in ignition.
3. What is the difference between a glow plug and a spark plug?
Glow plugs are used to pre-heat the air in a diesel engine for easy starting, while spark plugs in gasoline engines provide an electric spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
4. Do diesel engines have spark plugs for emissions control?
No, diesel engines do not use spark plugs, but they may be equipped with additional components like catalytic converters or diesel particulate filters to control emissions.
5. How does compression ignition work in diesel engines?
In diesel engines, compression ignition works by compressing air to a high pressure, which raises its temperature. When diesel fuel is injected into this hot air, it ignites spontaneously without the need for a spark.
Conclusion
Spark plugs are not used in diesel engines because of the fundamental differences in how gasoline and diesel engines operate. Diesel engines rely on compression ignition, where the high pressure generated in the cylinder causes the diesel fuel to ignite spontaneously without the need for an electrical spark.
The absence of spark plugs simplifies the design, increases fuel efficiency, and enhances the overall durability of diesel engines. Understanding these differences highlights the unique features of diesel engines and why they remain a popular choice for heavy-duty vehicles and machinery.